Sugarcane Farming Tips
Sugarcane crop thrives best in hot sunny tropical areas. The ideal climate for sugarcane is a long, warm growing season with a high incidence of solar radiation and adequate moisture in the soil. Areas with high rainfall and/or good irrigation are best suited for sugarcane cultivation.
Sugarcane can be successfully raised on diverse soil types ranging from sandy soils to clay loams & heavy clays. However, a well-drained, deep, loamy soil is considered ideal for sugarcane cultivation.
Soil should be ploughed using different tractor-drawn implements to obtain optimum soil tilth and prepare the ridges and furrows.
Under paired-row planting, 24,000 (2-budded setts) or 16,000 (3-budded setts) plants are required for planting 1 acre of land. Row to row spacing varies 90–120 cm depending on the soil texture.
Regular intercultural operations should be done to stir the soil in the furrows and remove the weeds. A partial hilling up of soil against crop rows is done when the cane crop starts rapid growth at the age of 3–4 months. Older leaves are removed to avoid attack of insect pests. The cane plants are also tied to prevent lodging of the canes as they grow.
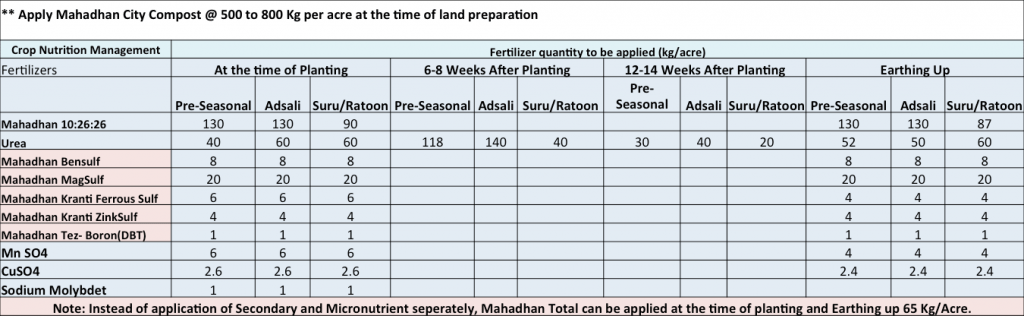
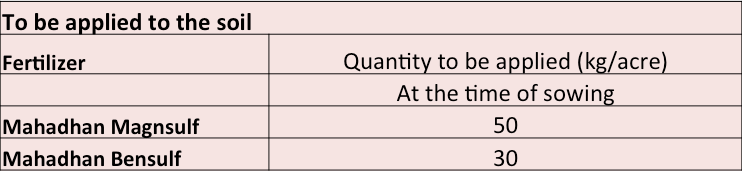
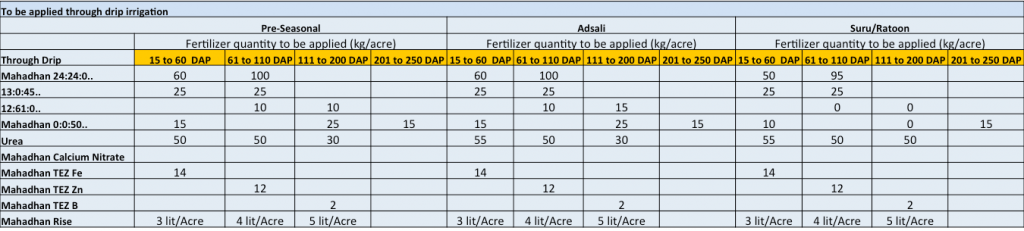
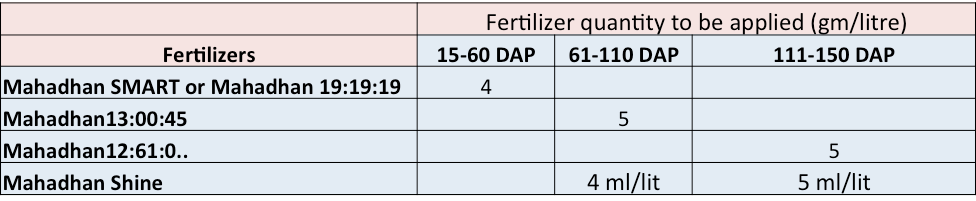
Sugarcane needs special attention with regards to its nutritional requirements. Farmers should apply required quantities of macro, secondary and micronutrients for better crop growth and higher yields along with sugar recovery. Deficiencies of N, P, K, S, Mg, Fe, Zinc, and Boron are often reported in sugarcane plantations. Hence, it is important that these nutrients are appropriately supplied through application of the right fertiliser at the right time.
Fertiliser schedule recommended for soil applications (Table 1):
Fertigation schedule (Table 2):
Foliar application recommended (Table 3):
Sugarcane requires regular irrigation at different stages. Provide shallow wetting with 2–3 cm depth of water at shorter intervals in the initial stage. During the later stages of tillering, grand growth and maturity phases, the irrigation intervals can be increased to 8–10 days.
Irrigation of sugarcane crop through drip system with fertiliser nutrient solutions (fertigation) could be adopted so that water as well as crop nutrition requirements could be met together.
Weeds
Sugarcane crop is also infested with weeds in the furrow areas, especially in the initial stages of growth. Most of the upland weeds are noticed in sugarcane crop.
Weed Management
- Regular intercultural operations including digging of ridges with a spade; 30, 60 and 90 days after planting
- Spraying of herbicide Atrazine (0.8 kg/ac) or Oxyflurofen (300 ml/ac) mixed in water (600 l/ha) as a pre-emergence herbicide on the third day of planting
- Post emergence directed spray application of glyphosate (1 l/ac) along with 2% ammonium sulphate or 2,4-D sodium salt (1 kg/ac) mixed in water (600 l/ha).
- If the parasitic weed striga is a problem, post-emergence application of 2,4-D sodium salt (kg/ha) mixed in water (500 l/ha) may be done.
- Early shoot borer Management
- Use resistant varieties & Intercropping of sugarcane with Daincha
- Trash mulching along the ridges to a thickness of 10-15 cm
- Removal and destruction of dead hearts. Install pheromone traps @ 10Nos. /ha
- Soil application of insecticides Carboryl +Sevidol 4% G 12.5 kg/ha, Carbofuron 3G 33 kg/ha or Spraying of Chlorpyriphos 1000 ml/ha.
- White Grub Management
- Provide adequate irrigation.
- Deep ploughing immediately after harvesting.
- Stagnating water for 24hrs in the field makes the grub come out from the soil.
- Collection and destruction the adult beetles
- Sugarcane Wholly Aphid
- Paired row system of planting.
- Rapping of canes all along the rows.
- Dipping of the seed sets in Chlorpyripos 20 EC solution (2 ml/lit) before planting.
- Soil application of phorate 10 G @ 5kg/ac or spraying of Acephate 75 SP @1g/lit or Chlorpyriphos 20 EC @ 2 ml/lit or Oxydemeton methyl 25 EC @ 1.3 ml/lit,
Fungus, bacteria and virus cause diseases to sugarcane crop. Some of the diseases of sugarcane crop and their suggested control measures are listed below.
- Red rot disease – Management
- Dipping of seedsets in 0.25% solution of Agallol or Aretan for 2-3 minutes
- Uproot the infected plants and burn them
- Smut – Management
- Sowing of resistant varieties.
- Carefully cut down the apex of the plant in such a way that spores do not spread and burn it out along with the uprooted affected plant.
- Wilt – Management
- Sowing of resistant varieties.
- Uproot the infected plants and bum them
- Early varieties have to be harvested at 10 to 11 months age.
- Mid-season varieties at 11 to 12 months
- Harvest the cane at peak maturity
- Cut the cane to the ground level for both plant and ratoon crops
Can we help you?