Soybean Farming Tips
Soybean thrives in a warm and moist climate. Day-length is a key factor in soybean varieties as they are short-day plants. Soybean requires well-drained and fertile soils with a pH range of 6–7.5. The best soil type is sandy loam with good organic matter content. Water logging soils are not suitable for soybean cultivation.
Soybean requires a good seedbed with a reasonably fine texture and not too many clods. Land should be well levelled and free from crop stubble. One deep ploughing with mould board plough followed by harrowing twice or ploughing twice with a local plough are sufficient. There should be optimum moisture in the field at the time of sowing.
On an average the seed rate adopted for soybean varies from 16–20 kg/ac depending on the spacing followed.
Rows are spaced 45 × 60 cm and
plants 4–5 cm apart
Intercultural operations, including hoeing once or twice, are helpful in keeping the field weed-free from the beginning.
Based on the nutritional needs of soybean crop, the following schedules are recommended for soil and foliar application of fertiliser, to improve yields and quality of soybean.
Fertiliser schedule recommended for soil applications
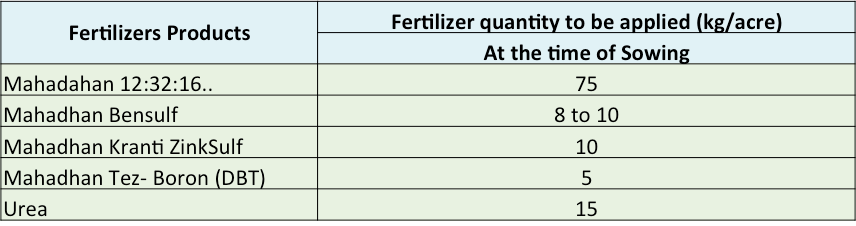
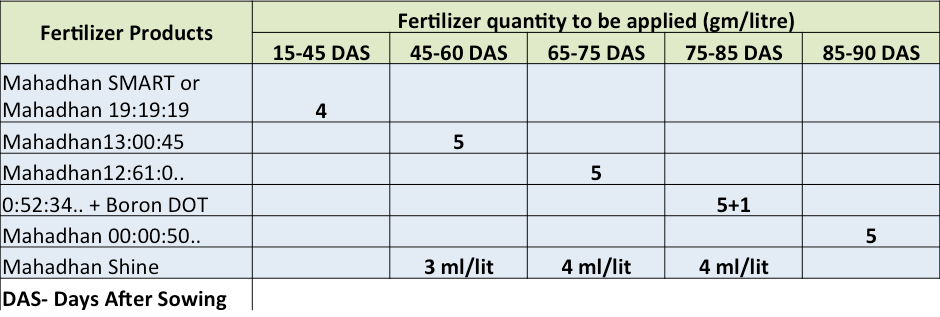
Foliar application schedule recommended
Soybean is grown during Kharif season, and due to high rainfall no irrigation is needed. However water stress should be avoided during flowering and pod formation stages of the crop.
Weeds
Both monocot and dicot weeds infest soybean crop. Echinocloa sp is a commonly occurring weed that causes significant yield loss unless it is effectively controlled.
Weed Management
- Spray application herbicides Imazethapyr 10 SL (1 l/ha) 15–20 DAS or Propaquizafop 10% EC (625 ml/ha) 15–20 DAS helps in controlling monocot weeds including Echinocloa sp.
- Application of a combination products like Propaquizafop with Imazethapyr MEA (2 l/ha) 15–20 DAS controls both dicots and monocots
- Other herbicides used for weed management in soybean are Diclosulam (84%), WDG (12.4 g/ac) 1–3 DAS, a combination of Fomesafen with Quizalofop EC (1 l/ha) 15–20 DAS or Chlorimuron ethyl (37.5 g/ha) 15–20 DAS.
- Management of Gram pod borer
- Install Pheromone traps
- Spray the crop with Ha NPV @ 250 LE/ha, (or)
- Quinalphos 25EC@ 1.5 l/ha, (or)
- Indoxacarb 14.5 SC @ 500 ml/ha.
- Management of Tobacco caterpillar
- Install Pheromone traps.
- Survey the field thoroughly and remove plant parts /plants having gregarious stage of caterpillars.
- Spray the crop with Sl NPV @ 250 LE/ha, or
- Spraying of insecticides like Quinalphos 25 EC @ 1.5 l/ha, or Indoxacarb 14.5 SC @ 500 ml/ha, or Spinetoram 11.7 SC @ 450 ml/ha
- Management of Soybean Stem fly
- Treat the seed with Thiamethoxam 30 FS @ 10g/kg seed
- Management of Semiloopers
- Application of recommended dose of fertilizers including Potash.
- Spraying of insecticides like Quinalphos 25 EC @ 1.5 l/ha or Chlorantraniliprole 20 SC @ 100 ml/ha or Indoxacarb 14.5 SC @ 500 ml/ha or pre-mix insecticide Betacyfluthrin + Imidacloprid @ 350 ml/ha.
- White fly Management
- Seed treatment of soybean with Thiamethoxam 30 FS @ 10 g per kg seed;
- Installation of Yellow Sticky Traps
- Removal of YMV infected soybean plants
- Spraying of pre-mix insecticide Betacyfluthrin + Imidacloprid @ 350 ml/ha for the control of white flies at later stage
Twenty-three diseases identified and classified in to major and minor based on their distribution economic significance. Myrothecium leaf spot, Alternaria leaf spot, rust, collar rot, pod and stem blight, anthracnose and pod blight, bacterial pustule, yellow mosaic and no podding syndrome were classified as major.
Management of Gram pod borer
- Sowing of disease-resistant lines/varieties
- Intercropping with maize and sorghum and pearl millet in 4:2 ratio
- Seed treatment with carboxin + thiram @ 2 g or thiram and carbendazim in the ratio of 2:1 @ 3g/kg seed
- Seed treatment with biocontrol agents viz. Trichoderma viride and Pseudomonas fluorescens
- Two spray applications of carbendazim or thiophanate methyl for the management of foliar diseases and spraying of fungicides like hexaconazole, propiconazle, triadimefon and oxycarboxin (0.1%) for managing the rust disease.
- When the plants reach maturity the leaves turn yellow and drop and soybean pods dry out quickly.
- At harvest, the moisture content of the seeds should be 15% or less.
Can we help you?